This codelab series focuses on the Fuchsia emulator (FEMU) as the target device, which is built and distributed with the source tree and runs on your development machine. However, you can also build Fuchsia for supported hardware platforms, such as an Intel NUC.
This section describes some specifics related to working with Fuchsia on physical devices.
Configure
Fuchsia defines support for hardware devices by the board name used to
configure the build. This includes any hardware-specific packages such as
drivers. Recall the fx set command used previously:
fx set workbench_eng.x64In this example, x64 is the board name that can run on FEMU and Intel NUC.
To build the same product for the Khadas VIM3, you can modify the set
command to use the vim3 board.
fx set workbench_eng.vim3Running fx build will now generate an image for the target device.
Bootstrap
Before flashing the operating system, a supported device must have a Fuchsia-compatible bootloader installed. This process is known as bootstrapping the device. Many devices have a compatible bootloader installed from the factory, others may require manufacturer-specific tools to update the bootloader to a compatible version. See the device documentation for more details regarding your specific device.
Flash
The process of loading the operating system onto the device is known as
flashing. With a device in bootloader mode connected to your workbench,
you can use the flash command to flash Fuchsia onto the device.
fx flashFor devices that have already been flashed, you can reboot them from Fuchsia
into bootloader mode if you need to flash them again using ffx:
ffx target reboot --bootloaderDiscover
You can discover and interact with Fuchsia devices from a development machine connected over USB or a local IPv6 network. Fuchsia enables automatic device discovery using DNS Service Discovery (DNS-SD) over multicast DNS (mDNS) and the Overnet mesh protocol.
Host tools such as ffx discover advertising devices and enable host-target
interaction with both physical devices and FEMU.
ffx target listNAME SERIAL TYPE STATE ADDRS/IP RCS
fuchsia-5254-0063-5e7a <unknown> . Product [fe80::c357:53e7:aedf:ed95%qemu] Y
If a target device does not advertise discovery packets or ffx is unable to
detect them, you can manage those targets manually using the add and remove
commands:
ffx target add device-ip:device-portffx target remove device-ip:device-port
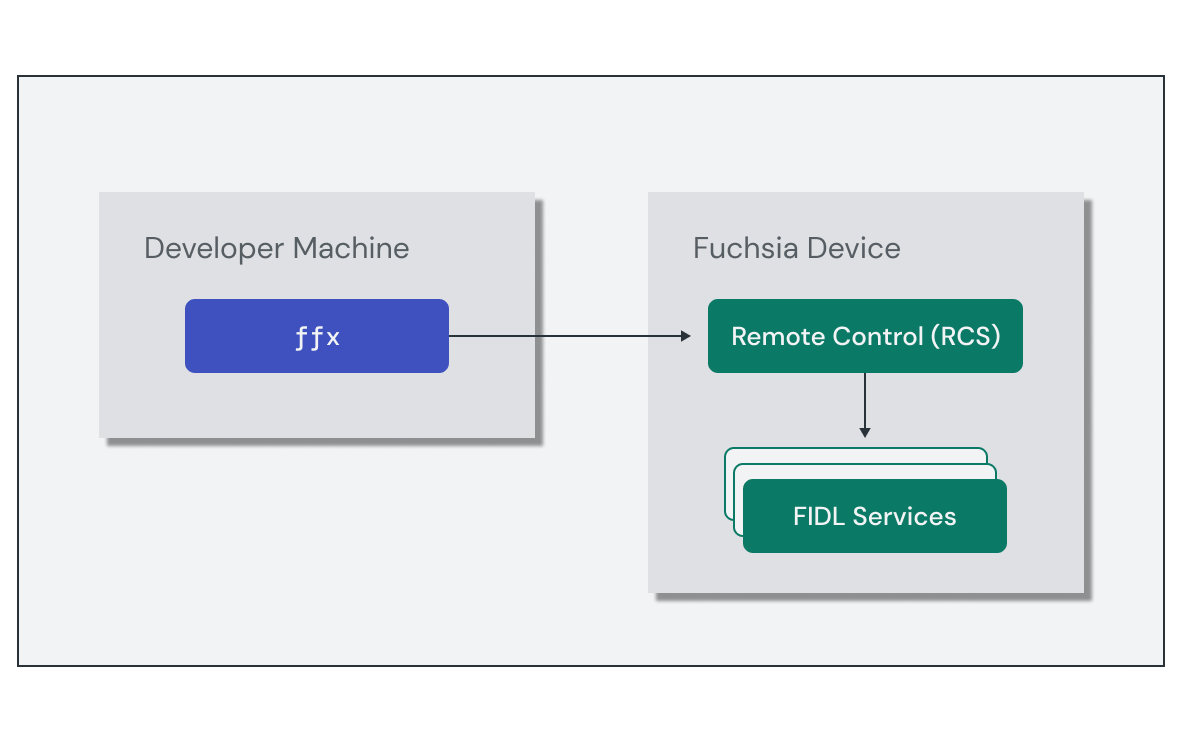
Once a device is tracked in the target list, ffx interacts with the Remove
Control Service (RCS) on the target to enable you to send additional commands.
What's Next?
Congratulations! You've successfully customized and built Fuchsia from source, and have a better understanding for where the key system components live in the source tree.
In the next module, you'll learn more about building Fuchsia's fundamental unit of software:
