每個元件都有宣告,可說明元件的屬性和功能。如果是套件中分發的元件,則會使用元件資訊清單檔案表示宣告,並透過元件解析器載入。
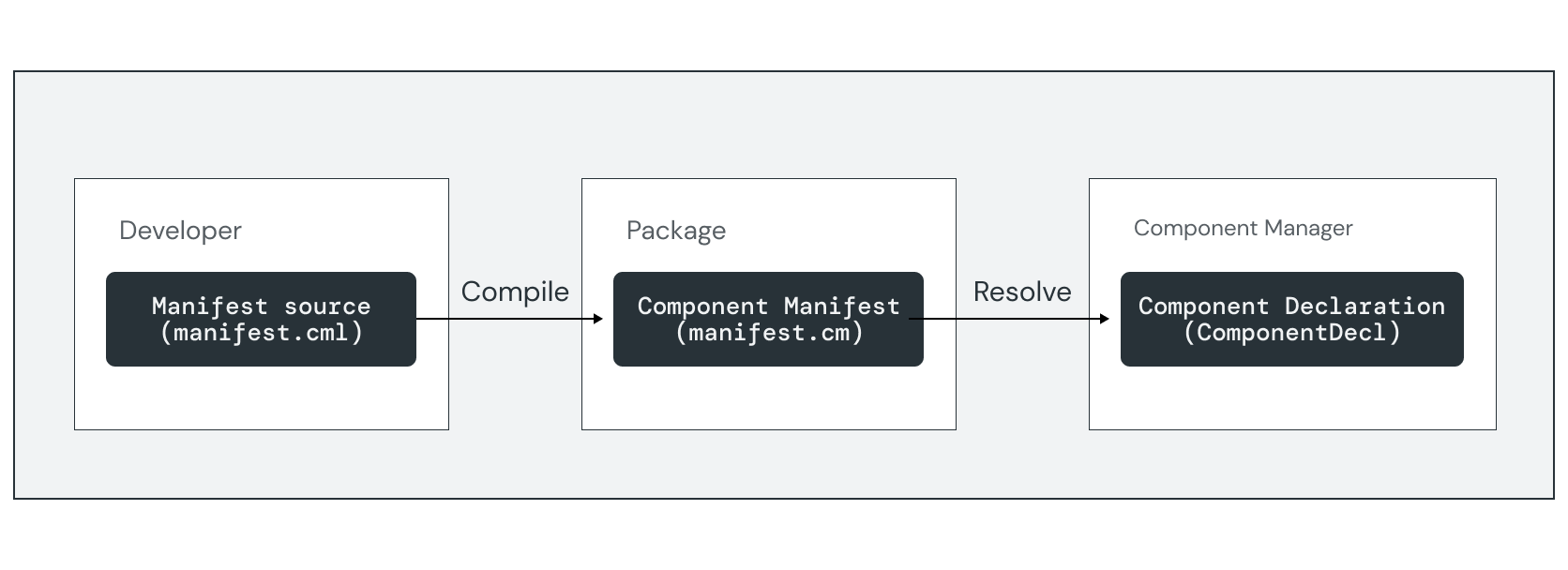
您可以使用元件資訊清單語言 (CML) 檔案宣告元件。在建構期間,元件資訊清單編譯器 (cmc) 工具會驗證並編譯資訊清單來源,轉換為二進位格式 (.cm),並儲存在元件的套件中。在執行階段,元件解析器會將二進位元件資訊清單載入 ComponentDecl FIDL 結構,以便
元件資訊清單
CML 檔案是結尾為 .cml 副檔名的 JSON5 檔案。以下是簡易元件執行 ELF 二進位檔的 CML 資訊清單檔案範例,該檔案會將「Hello, World」訊息輸出至系統記錄:
{
// Information about the program to run.
program: {
// Use the built-in ELF runner.
runner: "elf",
// The binary to run for this component.
binary: "bin/hello",
// Program arguments
args: [
"Hello",
"World!",
],
},
// Capabilities used by this component.
use: [
{ protocol: "fuchsia.logger.LogSink" },
],
}
這個檔案會宣告元件的兩個主要資訊區段:
program:說明可執行的資訊,例如二進位檔案、程式引數和相關的執行階段。在這個範例中,二進位檔會編譯為 ELF 可執行檔,並使用內建的 ELF 執行程式。use:宣告此元件執行所需的功能。在這個範例中,fuchsia.logger.LogSink通訊協定可讓元件將訊息寫入系統記錄 (syslog)。
資訊清單分割片
某些功能集合代表系統中許多元件的常見用途需求,例如記錄。為簡化在元件中加入這些功能的程序,架構會將這些功能抽象化為可納入 CML 來源檔案的資訊清單區塊。
以下是與前述範例等同的 CML。在這種情況下,您可以透過加入 diagnostics/syslog/client.shard.cml 而非明確宣告 fuchsia.logger.LogSink,提供必要的記錄功能:
{
include: [ "syslog/client.shard.cml" ],
// Information about the program to run.
program: {
// Use the built-in ELF runner.
runner: "elf",
// The binary to run for this component.
binary: "bin/hello-world",
// Program arguments
args: [
"Hello",
"World!",
],
},
}
建築零件
Fuchsia 建構系統會在 //build/components.gni 中提供範本做為 GN 匯入項目,以便建構並將軟體套件至 Fuchsia 元件。以下是簡單 C++ 元件的 BUILD.gn 檔案範例:
import("//build/components.gni")
executable("bin") {
sources = [ "main.cc" ]
}
resource("my_file") {
sources = [ "my_file.txt" ]
outputs = [ "data/{{source_file_part}}" ]
}
fuchsia_component("hello-world-component") {
component_name = "hello-world"
deps = [
":bin",
":my_file",
]
manifest = "meta/hello-world.cml"
}
fuchsia_package("hello-world") {
package-name = "hello-world"
deps = [
":hello-world-component",
]
}
這個檔案包含下列主要元素:
executable():將原始碼編譯為二進位檔案。這個目標會因程式設計語言而異。舉例來說,executable目標可用於 C++,rustc_binary可用於 Rust,go_binary可用於 Golang。resource():選用的命名資料檔案集合,可將其做為資源複製到其他 GN 目標。這些檔案可供元件命名空間中的二進位檔存取。fuchsia_component():將二進位檔、元件資訊清單和其他資源收集到單一目標中。這個目標會使用cmc將資訊清單來源編譯為元件宣告。fuchsia_package():元件的分發單位。允許一或多個元件託管在套件存放區中,並納入目標裝置的套件組合。這個目標會產生套件中繼資料,並建構 Fuchsia 封存檔 (.far) 檔案。
套件可包含多個元件,在 fuchsia_package() 範本中列為 deps。您可以使用 fuchsia_package_with_single_component() 範本,為只包含一個元件的套件簡化建構檔案。
以下簡化版 BUILD.gn 範例與前一個範例相同:
import("//build/components.gni")
executable("bin") {
sources = [ "main.cc" ]
}
resource("my_file") {
sources = [ "my_file.txt" ]
outputs = [ "data/{{source_file_part}}" ]
}
fuchsia_package_with_single_component("hello-world") {
manifest = "meta/hello-world.cml"
deps = [
":bin",
":my_file",
]
}
練習:建立新元件
在本練習中,您將建構並執行基本元件,該元件會讀取程式引數,並透過系統記錄回應問候訊息。
首先,請為 //vendor/fuchsia-codelab 目錄中名為 echo-args 的新元件建立專案鷹架:
mkdir -p vendor/fuchsia-codelab/echo-args在新專案目錄中建立下列檔案和目錄結構:
荒漠油廠
//vendor/fuchsia-codelab/echo-args
|- BUILD.gn
|- meta
| |- echo.cml
|
|- src
|- main.rs
BUILD.gn:GN 建構目標,適用於可執行的二進位檔、元件和套件。meta/echo.cml:宣告元件可執行檔和必要功能的資訊清單。src/main.rs:Rust 可執行二進位檔和單元測試的原始碼。
C++
//vendor/fuchsia-codelab/echo-args
|- BUILD.gn
|- meta
| |- echo.cml
|
|- echo_component.cc
|- echo_component.h
|- main.cc
BUILD.gn:GN 建構目標,適用於可執行的二進位檔、元件和套件。meta/echo.cml:宣告元件可執行檔和必要功能的資訊清單。echo_component.cc:C++ 元件功能的原始碼。main.cc:C++ 可執行二進位主項目點的原始碼。
新增程式引數
元件資訊清單檔案會定義元件可執行檔的屬性,包括程式引數和元件的功能。在 meta/echo.cml 中新增下列內容:
荒漠油廠
echo-args/meta/echo.cml:
{
include: [
// Enable logging on stdout
"syslog/client.shard.cml",
],
// Information about the program to run.
program: {
// Use the built-in ELF runner.
runner: "elf",
// The binary to run for this component.
binary: "bin/echo-args",
// Program arguments
args: [
"Alice",
"Bob",
],
// Program environment variables
environ: [ "FAVORITE_ANIMAL=Spot" ],
},
}
C++
echo-args/meta/echo.cml:
{
include: [
// Enable logging.
"syslog/client.shard.cml",
],
// Information about the program to run.
program: {
// Use the built-in ELF runner.
runner: "elf",
// The binary to run for this component.
binary: "bin/echo-args",
// Program arguments
args: [
"Alice",
"Bob",
],
// Program environment variables
environ: [ "FAVORITE_ANIMAL=Spot" ],
},
}
記錄引數
開啟主要可執行檔的來源檔案,然後新增下列匯入陳述式:
荒漠油廠
echo-args/src/main.rs:
use log::info;
C++
echo-args/main.cc:
#include <lib/syslog/cpp/log_settings.h>
#include <lib/syslog/cpp/macros.h>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include "vendor/fuchsia-codelab/echo-args/echo_component.h"
新增下列程式碼來實作 main() 函式:
荒漠油廠
echo-args/src/main.rs:
#[fuchsia::main(logging = true)]
async fn main() -> Result<(), anyhow::Error> {
// Read program arguments, and strip off binary name
let mut args: Vec<String> = std::env::args().collect();
args.remove(0);
// Include environment variables
let animal = std::env::var("FAVORITE_ANIMAL").unwrap();
args.push(animal);
// Print a greeting to syslog
info!("Hello, {}!", greeting(&args));
Ok(())
}
C++
echo-args/main.cc:
int main(int argc, const char* argv[], char* envp[]) {
fuchsia_logging::LogSettingsBuilder builder;
builder.WithTags({"echo"}).BuildAndInitialize();
// Read program arguments, and exclude the binary name in argv[0]
std::vector<std::string> arguments;
for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++) {
arguments.push_back(argv[i]);
}
// Include environment variables
const char* favorite_animal = std::getenv("FAVORITE_ANIMAL");
arguments.push_back(favorite_animal);
// Print a greeting to syslog
FX_LOG_KV(INFO, "Hello", FX_KV("greeting", echo::greeting(arguments).c_str()));
return 0;
}
這個程式碼會讀取程式引數,並將其傳遞至名為 greeting() 的函式,產生 syslog 項目的回應。
新增下列程式碼來實作 greeting() 函式:
荒漠油廠
echo-args/src/main.rs:
// Return a proper greeting for the list
fn greeting(names: &Vec<String>) -> String {
// Join the list of names based on length
match names.len() {
0 => String::from("Nobody"),
1 => names.join(""),
2 => names.join(" and "),
_ => names.join(", "),
}
}
C++
echo-args/echo_component.h:
#include <string>
#include <vector>
namespace echo {
std::string greeting(std::vector<std::string>& names);
} // namespace echo
echo-args/echo_component.cc:
#include "vendor/fuchsia-codelab/echo-args/echo_component.h"
#include <numeric>
namespace echo {
static std::string join(std::vector<std::string>& input_list, const std::string& separator) {
return std::accumulate(std::begin(input_list), std::end(input_list), std::string(""),
[&separator](std::string current, std::string& next) {
return current.empty() ? next : (std::move(current) + separator + next);
});
}
// Return a proper greeting for the list
std::string greeting(std::vector<std::string>& names) {
// Join the list of names based on length
auto number_of_names = names.size();
switch (number_of_names) {
case 0:
return "Nobody!";
case 1:
return join(names, "");
case 2:
return join(names, " and ");
default:
return join(names, ", ");
}
}
} // namespace echo
這個函式會根據清單長度,從提供的引數清單建立簡單字串。
新增至建構設定
在 BUILD.gn 檔案中更新程式的依附元件:
荒漠油廠
echo-args/BUILD.gn:
import("//build/components.gni")
import("//build/rust/rustc_binary.gni")
group("echo-args") {
testonly = true
deps = [
":package",
]
}
rustc_binary("bin") {
output_name = "echo-args"
edition = "2024"
# Generates a GN target for unit-tests with the label `bin_test`,
# and a binary named `echo_bin_test`.
with_unit_tests = true
deps = [
"//src/lib/fuchsia",
"//third_party/rust_crates:anyhow",
"//third_party/rust_crates:log",
]
sources = [ "src/main.rs" ]
}
fuchsia_component("component") {
component_name = "echo-args"
manifest = "meta/echo.cml"
deps = [ ":bin" ]
}
fuchsia_package("package") {
package_name = "echo-args"
deps = [ ":component" ]
}
C++
echo-args/BUILD.gn:
import("//build/components.gni")
group("echo-args") {
testonly = true
deps = [
":package",
]
}
executable("bin") {
output_name = "echo-args"
sources = [ "main.cc" ]
deps = [
":cpp-lib",
"//sdk/lib/async-default",
"//sdk/lib/async-loop:async-loop-cpp",
"//sdk/lib/async-loop:async-loop-default",
"//sdk/lib/syslog/cpp",
]
}
source_set("cpp-lib") {
sources = [
"echo_component.cc",
"echo_component.h",
]
}
fuchsia_component("component") {
component_name = "echo-args"
manifest = "meta/echo.cml"
deps = [ ":bin" ]
}
fuchsia_package("package") {
package_name = "echo-args"
deps = [ ":component" ]
}
將新的元件新增至建構設定:
fx set workstation_eng.x64 --with //vendor/fuchsia-codelab/echo-args執行 fx build,並確認建構作業是否順利完成:
fx build在下一節中,您將將此元件整合至建構項目,並測試系統記錄中的輸出內容。

