Integration testing scenarios involve two or more components operating in the same realm and exchanging capabilities. While the majority of tests are unit tests that span only a single component, integration testing scenarios call for defining realm topologies and capability routes.
Test Runner Framework integration
The integration test component integrates with the Test Runner Framework by including the test runner shard matching the supported language-specific testing framework.
Rust
include: [
"//src/sys/test_runners/rust/default.shard.cml",
"syslog/client.shard.cml",
],
// Information about the program to run.
program: {
// The binary to run for this component.
binary: "bin/echo_integration_test_rust",
},
C++
include: [
"//src/sys/test_runners/gtest/default.shard.cml",
"inspect/offer.shard.cml",
"syslog/client.shard.cml",
],
// Information about the program to run.
program: {
// The binary to run for this component.
binary: "bin/echo_integration_test_cpp",
},
This shard provides two key elements:
- Expose the
fuchsia.test.Suiteprotocol, required for the framework to discover and execute the test cases. - Set the program
runnerto the test runner provided for the given testing framework.
Test realm topology
The integration test component declares the topology of the test realm with itself as the parent. This allows the test controller to be responsible for capability routing between components under test and their dependencies.
The following is an example topology for integration testing the echo_server
component:
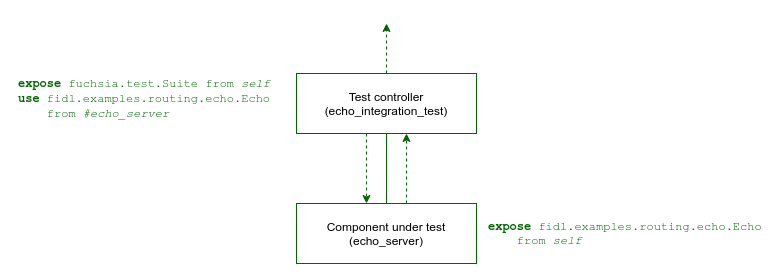
This is a simple test realm that binds to the fidl.examples.routing.echo.Echo
protocol exposed by the echo_server component.
The echo_integration_test package contains the following components:
- echo_integration_test - Test controller component
- echo_server - Component under test
You can define the test realm topology in the following ways:
- Realm Builder: Dynamically in code using the Realm Builder library.
- Component manifests: Statically using component manifest language (CML).
Use the following table to help determine which approach is best for your integration tests:
| Integration test cases | Realm Builder | Static CML |
|---|---|---|
| Simple integration tests with static dependencies | ||
| Unique component instances for each test case | ||
| Lifecycle of components under test bound to each test case | ||
| Dynamic fake, mock, and stub instances for components under test | ||
| Dynamic routing and configuration between test cases |
Realm Builder
In cases where realm topology needs to be defined at runtime, or components need to be replaced with local mock implementations, you can use the Realm Builder library to create the topology dynamically in your test code.
The test controller component's manifest includes the Realm Builder library using its component manifest shard:
Rust
include: [
"sys/component/realm_builder.shard.cml",
// ...
],
C++
include: [
"sys/component/realm_builder.shard.cml",
// ...
],
The test controller code constructs the test realm topology, adding echo_server as a
child component and declaring the necessary capability routes back to the parent:
Rust
use {
// ...
fuchsia_component_test::{
Capability, ChildOptions, LocalComponentHandles, RealmBuilder, Ref, Route,
},
futures::{StreamExt, TryStreamExt},
};
// ...
let builder = RealmBuilder::new().await?;
// Add component to the realm, which is fetched using a URL.
let echo_server = builder
.add_child(
"echo_server",
"fuchsia-pkg://fuchsia.com/realm-builder-examples#meta/echo_server.cm",
ChildOptions::new(),
)
.await?;
builder
.add_route(
Route::new()
.capability(Capability::protocol_by_name("fidl.examples.routing.echo.Echo"))
.from(&echo_server)
.to(Ref::parent()),
)
.await?;
C++
#include <lib/sys/component/cpp/testing/realm_builder.h>
// ...
RealmBuilder builder = RealmBuilder::Create();
// Add component server to the realm, which is fetched using a URL.
builder.AddChild("echo_server",
"fuchsia-pkg://fuchsia.com/realm-builder-examples#meta/echo_server.cm");
builder.AddRoute(Route{.capabilities = {Protocol{.name = "fidl.examples.routing.echo.Echo"}},
.source = ChildRef{"echo_server"},
.targets = {ParentRef()}});
The test controller code interacts with the echo_server through the capabilities
exposed by the created realm:
Rust
let realm = builder.build().await?;
let echo: fecho::EchoProxy = realm.root.connect_to_protocol_at_exposed_dir()?;
assert_eq!(echo.echo_string(Some("hello")).await?, Some("hello".to_owned()));
C++
RealmRoot realm = builder.Build(dispatcher());
zx::result<fidl::ClientEnd<fidl_examples_routing_echo::Echo>> client_end =
realm.component().Connect<fidl_examples_routing_echo::Echo>();
ASSERT_FALSE(client_end.is_error()) << client_end.status_string();
fidl::SyncClient echo_client(std::move(*client_end));
fidl::Result<::fidl_examples_routing_echo::Echo::EchoString> result =
echo_client->EchoString({"hello"});
ASSERT_EQ(result->response(), "hello");
For complete details on implementing tests using Realm Builder, see the Realm Builder developer guide.
Component manifests
In cases where all components in the test are static, you can define the entire topology for the test realm declaratively using CML in the component manifest for the test controller.
The test controller component's manifest statically declares the echo_server
component under test as a child, and routes the necessary capabilities back to
the parent:
Rust
{
include: [
"//src/sys/test_runners/rust/default.shard.cml",
"syslog/client.shard.cml",
],
// Information about the program to run.
program: {
// The binary to run for this component.
binary: "bin/echo_integration_test_rust",
},
// Child components orchestrated by the integration test.
children: [
{
name: "echo_server",
url: "#meta/echo_server.cm",
},
],
// Capabilities used by this component.
use: [
{
protocol: [ "fidl.examples.routing.echo.Echo" ],
from: "#echo_server",
},
],
// Capabilities required by components under test.
offer: [
{
dictionary: "diagnostics",
from: "parent",
to: "#echo_server",
},
],
}
C++
{
include: [
"//src/sys/test_runners/gtest/default.shard.cml",
"inspect/offer.shard.cml",
"syslog/client.shard.cml",
],
// Information about the program to run.
program: {
// The binary to run for this component.
binary: "bin/echo_integration_test_cpp",
},
// Child components orchestrated by the integration test.
children: [
{
name: "echo_server",
url: "#meta/echo_server.cm",
},
],
// Capabilities used by this component.
use: [
{
protocol: [ "fidl.examples.routing.echo.Echo" ],
from: "#echo_server",
},
],
}
The test controller code interacts with the echo_server through its exposed
capabilities:
Rust
use anyhow::Error;
use fidl_fidl_examples_routing_echo as fecho;
use fuchsia_component::client;
#[fuchsia::test]
async fn echo_integration_test() -> Result<(), Error> {
const ECHO_STRING: &str = "Hello, world!";
let echo = client::connect_to_protocol::<fecho::EchoMarker>()
.expect("error connecting to echo server");
let out = echo.echo_string(Some(ECHO_STRING)).await.expect("echo_string failed");
assert_eq!(ECHO_STRING, out.unwrap());
Ok(())
}
C++
#include <fidl/examples/routing/echo/cpp/fidl.h>
#include <lib/fidl/cpp/string.h>
#include <lib/sys/cpp/component_context.h>
#include <string>
#include <gtest/gtest.h>
TEST(EchoIntegrationTest, TestEcho) {
::fidl::examples::routing::echo::EchoSyncPtr echo_proxy;
auto context = sys::ComponentContext::Create();
context->svc()->Connect(echo_proxy.NewRequest());
::fidl::StringPtr request("Hello, world!");
::fidl::StringPtr response = nullptr;
ASSERT_TRUE(echo_proxy->EchoString(request, &response) == ZX_OK);
ASSERT_TRUE(request == response);
}
Test package
All components under test are included in the same hermetic test package. This promotes the ability to run and update tests in different environments without concern for dependencies falling out of sync.
See the following BUILD.gn file that defines a fuchsia_test_package() target for this example:
Rust
rustc_test("bin") {
name = "echo_integration_test_rust"
edition = "2024"
deps = [
"//examples/components/routing/fidl:echo_rust",
"//src/lib/fuchsia",
"//src/lib/fuchsia-component",
"//third_party/rust_crates:anyhow",
]
sources = [ "src/lib.rs" ]
}
fuchsia_component("echo_integration_test_component") {
testonly = true
component_name = "echo_integration_test"
manifest = "meta/echo_integration_test.cml"
deps = [ ":bin" ]
}
fuchsia_test_package("echo_integration_test_rust") {
test_components = [ ":echo_integration_test_component" ]
deps = [ "//examples/components/routing/rust/echo_server:echo_server_cmp" ]
}
C++
executable("bin") {
output_name = "echo_integration_test_cpp"
sources = [ "echo_integration_test.cc" ]
deps = [
"//examples/components/routing/fidl:echo_hlcpp",
"//sdk/lib/async-loop:async-loop-cpp",
"//sdk/lib/async-loop:async-loop-default",
"//sdk/lib/sys/cpp",
"//sdk/lib/sys/cpp/testing:unit",
"//src/lib/fxl/test:gtest_main",
"//third_party/googletest:gtest",
]
testonly = true
}
fuchsia_component("echo_integration_test_component") {
testonly = true
component_name = "echo_integration_test"
manifest = "meta/echo_integration_test.cml"
deps = [ ":bin" ]
}
fuchsia_test_package("echo_integration_test_cpp") {
test_components = [ ":echo_integration_test_component" ]
deps = [ "//examples/components/routing/cpp/echo_server:echo_server_cmp" ]
}
Components are built into the fuchsia_test_package() using the following variables:
test_components: Components containing tests that expose thefuchsia.test.Suiteprotocol.deps: Additional component dependencies required by the integration test.
For more details, see Test package GN templates.
Test component monikers
A component's moniker identifies the unique instance in the component topology.
For components running inside of a test topology, the moniker path is relative to
the root component in the test realm. In the above example, the root component is
the test controller component that exposes the fuchsia.test.Suite protocol.
The child moniker format depends on your test realm topology:
- Static CML: Components declared statically as children of the root test controller
are simply identified by their component
name. - Realm Builder: Realm Builder introduces an intermediate collection between the test controller and child components. For more details on test component monikers with Realm Builder, see the Realm Builder developer guide.
