This guide shows you ways to test the hardware subsystems of a physical Fuchsia device.
Intended audience of this guide
This guide assumes that you're familiar with hardware and low-level software development.
Overview
All of the Fuchsia hardware testing workflows in this guide assume
that your Fuchsia device is connected to a test host. The
test host is a laptop or desktop running Linux or Windows.
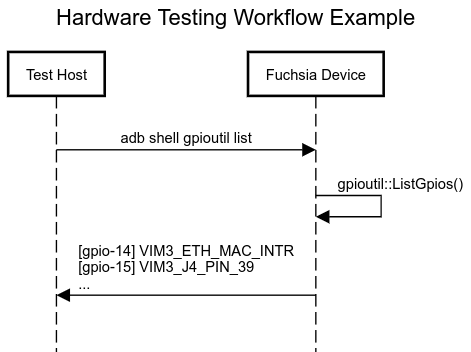
To test a hardware subsystem of your Fuchsia device you run a command
like adb shell gpioutil list on the test host. The first part of the command,
adb shell, is the transport system that handles communication between
your test host and Fuchsia device. The second part of the command,
gpioutil list, is the testing tool that actually exercises or queries
a hardware subsystem on your Fuchsia device.
Supported setups
The OS of your test host determines what transport systems you
can use. For example, currently only adb is supported
on Windows. The following table shows what combinations of test
host OS and transport system are supported:
| Test Host OS | ffx |
adb |
UART |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linux | |||
| Windows |
The transport system determines what kind of physical connection
you can use between your test host and target device. For example,
adb requires a USB connection between the test host and Fuchsia
device. The hardware layout of your Fuchsia device also determines
what transport system you can use. For example, if your Fuchsia device
doesn't expose GND, TX, and RX pins, then you can't use UART.
Configuring Fuchsia builds for hardware testing
This section provides guidance for people who need to build a Fuchsia image with hardware testing tools enabled from source. If you already have a Fuchsia image with the tools you need then you can skip this section.
Building Fuchsia from source
If you've never built Fuchsia from source and need help with the basic workflows, see the following tutorials:
Including hardware testing tools in your build
If you try running a hardware testing tool (like gpioutil for example)
and get a not found error, it probably means that the hardware
testing tool was not enabled when your Fuchsia image was built.
Example:
-v: 1: gpioutil: not found
To fix this, try adding --with-base //bundles/tools to your fx set
call:
fx set PRODUCT.BOARD --with-base '//bundles/tools'The --with-base option adds all of the dependencies listed in
//bundles/tools/BUILD.gn as base packages in your Fuchsia image.
Most of Fuchsia's hardware testing tools are in this bundle.
Include a single tool directly
If the hardware testing tool you need is not listed in //bundles/tools/BUILD.gn
try setting the --with-base value to the path to the hardware testing
tool's BUILD.gn file. For example, the gpioutil build file is located at
//src/devices/gpio/bin/gpioutil/BUILD.gn. You can directly include gpioutil
as a base package with the following fx set command:
fx set PRODUCT.BOARD --with-base '//src/devices/gpio/bin/gpioutil'You can repeat the --with-base option as many times as needed:
fx set PRODUCT.BOARD \
--with-base '//src/devices/gpio/bin/gpioutil' \
--with-base '//src/media/audio/tools/audio-driver-ctl'Include adb
To enable adb in your Fuchsia image, you will need to include the
adb function driver and a daemon.
The daemon can be the Fuchsia adb daemon
or any other daemon that speaks to the function driver.
Running commands
As explained in Overview, you send commands from
your test host to your Fuchsia device over a transport system
like ffx, adb, or UART. This section provides more detail
about how to run commands with each transport system.
A key difference between transport systems: capabilities
The underlying component that powers each transport system affects what features are available to you. Different components expose different capabilities .
The capabilities available in ffx are determined by
the component you're exploring. The capabilities available in
adb and UART are determined by console-launcher,
which is the underlying component that powers those shells.
ffx
ffx is Fuchsia's main tool
for host-target interactions.
To start an interactive shell:
ffx component explore COMPONENT -l namespaceTo run single commands (gpioutil list for example):
ffx component explore COMPONENT -l namespace -c 'gpioutil list'UART
Most Fuchsia
boards
support
3-pin (TX, RX, GND) UART communication. They usually expect the
typical 115200 8N1
UART configuration. To send commands from your test host to your
Fuchsia device you'll need a serial console like minicom or
fx serial.
adb
If your Fuchsia image included adb then you can send
commands from your test host to your Fuchsia device with adb.
To start an interactive shell:
adb shellTo run single commands (gpioutil list for example):
adb shell 'gpioutil list'Fuchsia only has partial support for adb by design. See RFC-0200 for
details on what's supported and what's not. See
//src/developer/adb/bin/README.md
for more guidance on using adb with Fuchsia.
List of hardware testing tools
The following table points you to the specific tools that you can use to test out the various hardware subsystems on your Fuchsia device.
| Hardware subsystem | Tools |
|---|---|
| Audio | |
| GPIO | |
| I2C | |
| Lights |
