Components interact with one another through capabilities . A capability combines access to a resource and a set of rights, providing a access control and a means for interacting with the resource. Fuchsia capabilities typically access underlying kernel objects through handles provided in the component's namespace .
A component can interact with the system and other components only through the discoverable capabilities from its namespace and the few numbered handles it receives.
Capability routing
Components declare new capabilities that they offer to the system and capabilities provided by other components (or the framework) that they require in their component manifest. Component framework uses these declarations to populate the namespace.
For capabilities to be available at runtime, there must also be a valid capability route from the consuming component to a provider. Since capabilities are most often routed through parent components to their children, parent components play an important role in defining the sandboxes for their child components.
Some capability types are routed to environments rather than individual component instances. Environments configure the behavior of the framework for the realms where they are assigned. Capabilities routed to environments are accessed and used by the framework. Component instances do not have runtime access to the capabilities in their environment.
The availability feature lets components declare expectations about the circumstances under which they expect capabilities to be available.
Routing terminology
Routing terminology divides into the following categories:
- Declarations of how capabilities are routed between the component, its
parent, and its children:
offer: Declares that the capability listed is made available to a child component instance or a child collection.expose: Declares that the capabilities listed are made available to the parent component or to the framework. It is valid toexposefromselfor from a child component.
- Declarations of capabilities consumed or provided by the component:
use: For executable components, declares capabilities that this component requires in its namespace at runtime. Capabilities are routed from theparentunless otherwise specified, and each capability must have a valid route from its source.capabilities: Declares capabilities that this component provides. Capabilities that are offered or exposed fromselfmust appear here. These capabilities often map to a node in the outgoing directory .
Cycle detection
The component framework enforces that capababilities offered between components
do not form a cycle. The simplest example of a cycle would be a component that
offers a capability from child A to child B, and from B to A, without
the weak option.
Cycles are detected between:
- Child components and their parents.
- The current component and its children.
The current component is allowed to:
usecapabilities from its children, unless it is offering capabilities to those children.usea capability from its parent.exposea capability to its parent.
If there is a cycle, there are several strategies to address this.
- Mark one of the links as
dependency: "weak". Weak capabilities do not count as a dependency with respect to cycle detection or shutdown ordering. A component using a capability weakly should be programmed to operate correctly if the weak capability does not exist or goes away. - Split one of the components into two smaller components that do not have a cycle.
- Invert the order of one of the dependencies. For example, instead of
Busing a capability fromA,Acould use a second capability fromB. This can be done by adding a new capability toAandB's manifest, and then adding a newusetoA's manifest.
Capability types
The following capabilities can be routed:
| type | description | routed to |
|---|---|---|
protocol |
A filesystem node that is used to open a channel backed by a FIDL protocol. | components |
service |
A filesystem directory that is used to open a channel to one of several service instances. | components |
directory |
A filesystem directory. | components |
storage |
A writable filesystem directory that is isolated to the component using it. | components |
dictionary |
A capability that bundles other capabilities together. | components |
resolver |
A capability that, when registered in an environment, causes a component with a particular URL scheme to be resolved with that resolver. | environments |
runner |
A capability that, when registered in an environment, allows the framework to use that runner when starting components. | environments |
Examples
Consider the following example that describes capability routing through the component instance tree:
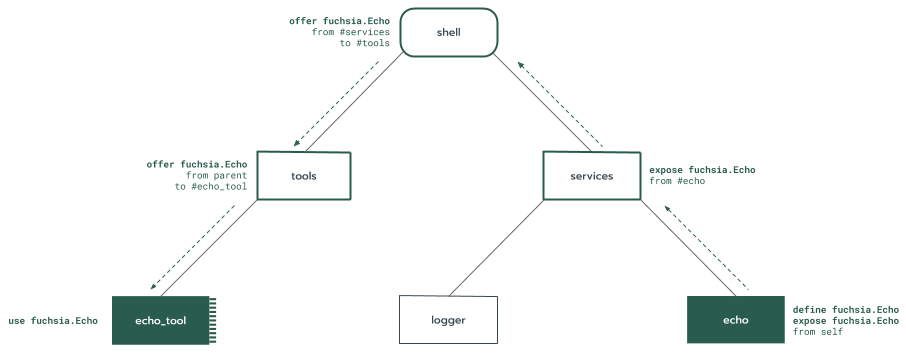
In this example:
- The
echocomponent instance provides thefuchsia.Echoprotocol as one of its declared capabilities. - The
echo_toolcomponent instance requires the use of thefuchsia.Echoprotocol capability.
Each intermediate component cooperates to explicitly route fuchsia.Echo from
echo to echo_tool:
echoexposesfuchsia.Echofromselfso the protocol is visible to its parent,services.servicesexposesfuchsia.Echofrom its childechoto its parent,shell.shelloffersfuchsia.Echofrom its childservicesto another child,tools.toolsoffersfuchsia.Echofromparentto its child,echo_tool.
Component Framework grants the request from echo_tool to use fuchsia.Echo
because a valid route is found to a component providing that protocol
capability.
For more information on how components connect to capabilities at runtime, see Life of a protocol open.
