| RFC-0210:虚拟化功能路由 | |
|---|---|
| 状态 | 已接受 |
| 区域 |
|
| 说明 | 定义虚拟化功能在平台和产品之间的路由方式。 |
| 问题 | |
| Gerrit 更改 | |
| 作者 | |
| 审核人 | |
| 提交日期(年-月-日) | 2022-11-07 |
| 审核日期(年-月-日) | 2023-02-23 |
摘要
本文档介绍了我们将如何将创建虚拟机的功能路由到产品会话。本文档还将介绍 Fuchsia 平台中包含的一组虚拟化功能和 API,以及产品提供的组件。
设计初衷
目前,所有虚拟化组件均由 Fuchsia 核心平台提供,包括:
- 用于模拟虚拟机和虚拟设备的组件
- 提供特定客机操作系统二进制文件的软件包
- 将适用于房客的功能与产品集成的组件
这会带来一些显著的缺点。通过将所有特定于访客的组件放置在平台中,我们使产品无法以产品专用的方式集成虚拟化。此外,许多访客会保留状态并持有用户数据,因此我们需要确保这些用户数据与所有其他用户数据一起加密和保护。本文档介绍了一种与产品无关的设计,但在设计过程中,我们会以工作站产品的要求为例子。
此提案的明确目标是实现将虚拟化作为 Fuchsia 平台功能提供。这意味着,我们将向产品会话公开一组功能,以便产品能够利用虚拟化机制,而无需将虚拟化所需的所有低级特权功能路由到会话本身。这在一定程度上基于 RFC-0092 - 会话和 RFC-0194 - 附录:会话中的指南。如需详细了解,请参阅安全注意事项。
利益相关方
哪些人对此 RFC 的接受与否有利益相关?(此部分为可选部分,但建议填写。)
教员:
由 FEC 任命的负责引导此 RFC 完成 RFC 流程的人员。
Reviewers:
- abdulla
- alerad
- dahastin
- jsankey
- aaronwood
- ypomortsev
咨询了:
列出应审核 RFC 但无需获得其批准的人员。
社交:
我们已在虚拟化、组件框架和安全方面的利益相关方中推广了该计划的草稿。
术语库
- 虚拟机管理器 (vmm):负责模拟和驱动虚拟机的组件。
- 虚拟设备:负责模拟单个设备(例如分块、网络等)的组件。
- vsock:一种准虚拟化套接字设备,允许在客户机和主机之间建立无配置套接字连接。通常用作虚拟机的控制平面。
背景
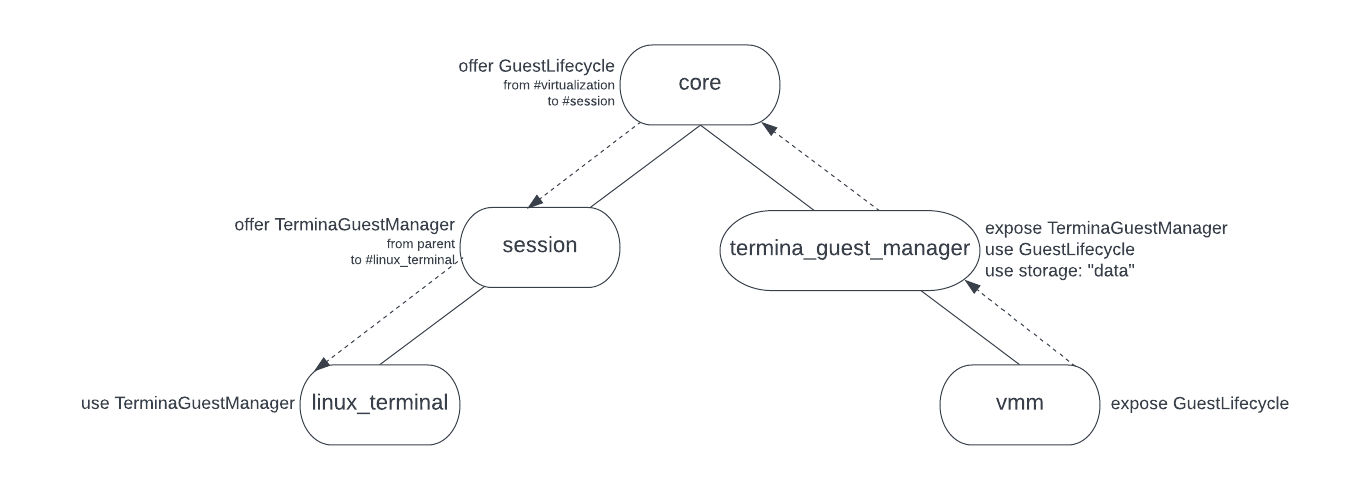
Fuchsia 上的虚拟机由 vmm(虚拟机管理器)组件驱动。vmm 组件本身会管理多个实现虚拟设备的子组件(例如 virtio_block.cm、virtio_net.cm 等),但本文档将整个组件群组统称为 vmm。vmm 将为虚拟机提供基本资源(内存、vCPU)和虚拟设备。vmm 组件与客机无关,并且没有任何特定于客机操作系统的逻辑。每个 vmm 组件实例由特定于来宾操作系统的 GuestManager 组件(例如 TerminaGuestManager)管理。GuestManager。包含针对访客生命周期以及任何访客专用服务或功能的更高级别逻辑。GuestManager 负责提供所有启动资源(内核、ramdisk、块设备等)以及来宾配置,例如要提供哪些设备、要提供多少个虚拟 CPU 或要提供多少内存。
Fuchsia 上支持的每个客机操作系统目前完全使用静态组件路由进行建模。例如,TerminaGuestManager 组件(为工作站上的 Linux 终端提供支持的客机)有一个由核心分片提供的静态子 vmm 组件。有些路线允许会话中的 Linux 终端组件连接到核心领域中的 TerminaGuestManager,有些路线则允许访客在图形界面中创建窗口(使用 virtio-wayland)。
存储
GuestManager 组件负责打开 vmm 所需的所有文件和设备;vmm 本身只会接收文件、块设备或其他有状态功能的句柄。TerminaGuestManager 将通过在 CFv2 data 存储功能提供的目录中创建文件来初始化有状态分区。其他只读有状态分区是通过打开 TerminaGuestManager 软件包本身包含的映像的 blobfs 文件提供的。
由于 TerminaGuestManager 是核心领域中的组件,因此将向其提供的 data 存储功能也来自核心领域。这意味着,在工作站等产品中,如果存在根据用户身份验证因素加密的单独账号卷,访客数据存储空间将不会位于此卷上,即使其中可能包含敏感用户数据也是如此。此外,假设我们有一个多用户系统,在核心领域中只有一个组件,这意味着只有一个 vmm 实例,并且数据会在所有账号之间共享,这不是一个可行的解决方案。
设计
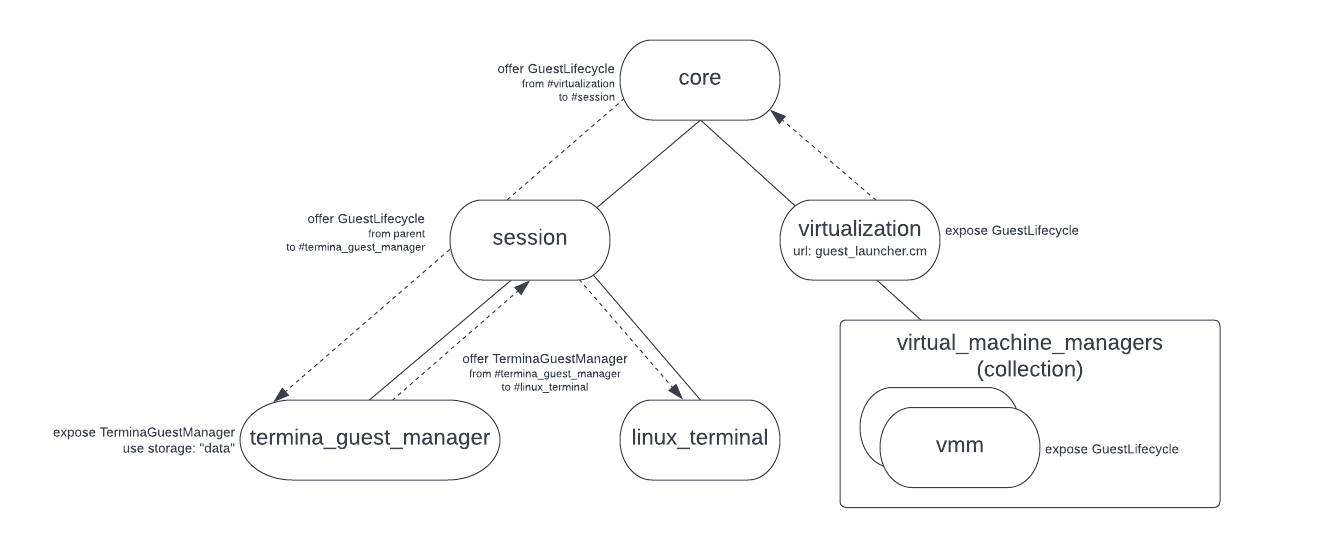
由于 vmm 组件需要多项特权功能,因此最好将其保留在核心中。此外,由于 vmm 提供了启动虚拟机的机制,因此 vmm 中已不再有产品专用政策或行为。从核心中提取 GuestManager 组件是可取的,因为这些是特定于产品的软件包,可带来仅与特定产品相关的逻辑和来宾操作系统。通过将这些组件从 core 中移出,我们可以让产品自由地以产品专用的方式自定义虚拟化集成方式,而无需处理虚拟机模拟的低级细节。
我们将引入一个新的核心分片,让会话可以在 CFv2 集合中创建 vmm 组件实例,但所有状态都必须由客户端提供和管理。然后,我们将提供使用 capability 路由启动虚拟机的功能,而不是使用每个 GuestManager 组件的静态子项 vmm.cm。这样,我们就可以将 GuestManager 组件移至会话,而无需将 vmm 本身也移至会话。换句话说,我们会保留 vmm,它在 core 中不依赖于产品和访客,并将产品专用 GuestManagers 移至会话中。
为此,我们将引入一个新的 VmmLauncher 组件来处理创建 vmm 组件。此组件将公开与 vmm 公开的相同 GuestLifecycle 协议。不同之处在于,VmmLauncher 不会直接实现 GuestLifecycle,而是会为每个 GuestLifecycle 连接创建一个新的 vmm 实例,并将 FIDL 通道的服务器端转发到新组件。GuestLifecycle 协议用于初始化虚拟机,然后开始执行。
/// The guest control plane allows for creating, starting, and stopping the guest.
protocol GuestLifecycle {
/// Create a VMM configured with the provided config. This instantiates all
/// devices and loads the kernel without starting the VCPU or device dispatch
/// loops.
///
/// `Create` must not be called after a call to `Run` until `Stop` is called.
/// Once a guest has been stopped with a call to `Stop`, then `Create` may be
/// called again to re-initialize the guest.
Create(resource struct {
guest_config GuestConfig;
}) -> (struct {}) error GuestError;
/// Binds to the Guest protocol for an initialized guest.
///
/// This operation must be called between `Create` and `Stop`, otherwise
/// the provided channel will be immediately closed.
Bind(resource struct {
guest server_end:Guest;
}) -> (struct {}) error GuestError;
/// Start the VCPU and device dispatch loops. This will not return until the
/// dispatch loops exit. On a clean shutdown (either guest or client initiated)
/// this will return success.
///
/// If forced to stop by the guest manager calling stop, a SHUTDOWN_FORCED
/// error will be returned. This will also return any runtime error that forces
/// the guest to stop.
///
/// `Run` must only be called after a call to `Create`. Once a guest is stopped with
/// a call to `Stop`, then `Run` may not be called again until `Create` is called
/// to re-initialize the guest. Notably, we do not support calling `Stop`
/// and then `Run` directly; the call to `Create` after `Stop` is a requirement.
Run() -> (struct {}) error GuestError;
/// Stop a running VMM. Returns once the dispatch loops have stopped. After
/// Stop returns, `Create` and then `Run` can be called again.
Stop() -> ();
};
type GuestError = strict enum {
/// Catch all VMM error.
INTERNAL_ERROR = 1;
/// A device endpoint was requested via the guest client API, but the device isn't enabled.
DEVICE_NOT_PRESENT = 2;
/// The config failed VMM validation for reasons such as a missing required field.
BAD_CONFIG = 3;
/// The VMM failed to initialize the guest object, usually due to capability routing issues
/// or memory layout problems.
GUEST_INITIALIZATION_FAILURE = 4;
/// The VMM failed to initialize a device.
DEVICE_INITIALIZATION_FAILURE = 5;
/// The VMM failed to start a device, usually because the device component returned a failure.
DEVICE_START_FAILURE = 6;
/// Two or more devices have attempted to register overlapping memory ranges.
DEVICE_MEMORY_OVERLAP = 7;
/// Failed to connect to a required service. Check the routing in the manifest.
FAILED_SERVICE_CONNECT = 8;
/// Failed to add a public service.
DUPLICATE_PUBLIC_SERVICES = 9;
/// General error when loading the guest kernel.
KERNEL_LOAD_FAILURE = 10;
/// Error when starting a VCPU.
VCPU_START_FAILURE = 11;
/// A VCPU encountered a fatal error while running.
VCPU_RUNTIME_FAILURE = 12;
/// The VMM was asked to run before it was created.
NOT_CREATED = 13;
/// A VMM is already running. The VMM must be stopped and a new VMM must be created before it
/// can be run again.
ALREADY_RUNNING = 14;
/// A running VMM was forced to stop by the VMM controller.
CONTROLLER_FORCED_HALT = 15;
};
向客户端公开以进行配置的一组参数包含在 GuestConfig FIDL 表中。这样,您就可以配置机器形状(vCPU 和内存)以及可用的虚拟设备。
type GuestConfig = resource table {
/// Type of kernel to load.
1: kernel_type KernelType;
/// File to load the kernel from.
2: kernel client_end:fuchsia.io.File;
/// File to load the initial RAM disk from.
3: ramdisk client_end:fuchsia.io.File;
/// File to load the dtb overlay for a Linux kernel from.
4: dtb_overlay client_end:fuchsia.io.File;
/// Kernel command-line to use.
5: cmdline string:MAX;
/// Additional kernel command-lines to append to the main command-line.
6: cmdline_add vector<string:MAX>:MAX;
/// The number of CPUs to provide to a guest.
7: cpus uint8;
/// Amount of guest memory required, in bytes. This value may be rounded up
/// depending on the system configuration.
8: guest_memory uint64;
/// A list of block devices to give a guest. Cannot be changed from the
/// command-line.
9: block_devices vector<BlockSpec>:MAX_BLOCK_DEVICES;
/// A list of specifications for network devices.
10: net_devices vector<NetSpec>:MAX_NET_DEVICES;
/// Optional virtio-wl device.
11: wayland_device WaylandDevice;
/// Optional virtio-magma device.
12: magma_device MagmaDevice;
/// Whether to add a default network device.
13: default_net bool;
/// Enable virtio-balloon.
14: virtio_balloon bool;
/// Enable virtio-console.
15: virtio_console bool;
/// Enable virtio-gpu.
16: virtio_gpu bool;
/// Enable virtio-rng.
17: virtio_rng bool;
/// Enable virtio-vsock.
18: virtio_vsock bool;
/// Enable virtio-sound.
19: virtio_sound bool;
/// Enable input streams (capture) for virtio-sound.
20: virtio_sound_input bool;
/// Host ports to listen for guest initiated vsock connections on. This can be
/// used for simplicity if a Listener is known at config creation time, or if a
/// Listener must be available at the moment of guest creation for timing
/// reasons.
/// To add a Listener after a guest starts, see HostVsockEndpoint::Listen.
21: vsock_listeners vector<Listener>:MAX;
};
Guest 协议可从虚拟机访问运行时服务。
/// A `Guest` provides access to services of a guest instance.
protocol Guest {
/// Get a guest console.
///
/// The details regarding what output is produced and what input is accepted
/// are determined by each guest, but will typically be a read/write socket
/// with a shell.
///
/// Returns ZX_ERR_UNAVAILABLE if the guest has no configured console.
GetConsole() -> (resource struct {
socket zx.handle:SOCKET;
}) error zx.status;
/// Get the socket for low-level guest debug logs.
///
/// The details regarding what output is produced and what input is accepted
/// are determined by each guest, but will typically be a read-only socket
/// with the guest kernel's serial logs.
GetSerial() -> (resource struct {
socket zx.handle:SOCKET;
}) error zx.status;
/// Get the vsock endpoint for the guest.
///
/// This endpoint can be used to register listeners for guest initiated
/// connections, and to initiate connections from a client. If listeners need
/// to be registered before the guest starts so that they are immediately
/// available, set them via the `GuestConfig` instead of using this protocol.
///
/// Returns error VSOCK_NOT_PRESENT if the guest was started without a vsock
/// device.
GetHostVsockEndpoint(resource struct {
endpoint server_end:HostVsockEndpoint;
}) -> (struct {}) error GuestError;
/// Get the balloon controller endpoint for the guest.
///
/// Returns error BALLOON_NOT_PRESENT if the guest was started without a
/// balloon device.
GetBalloonController(resource struct {
controller server_end:BalloonController;
}) -> (struct {}) error GuestError;
};
实现
我们将使用核心中名为 vmm_launcher.cm 的组件实现 VmmLauncher。此组件将管理一个 CFv2 集合,并将 vmm 组件启动到该集合中。然后,GuestManager 组件将更新为通过其 "parent"(而非通过静态子项)访问 GuestLifecycle capability。vmm_launcher.cm 将使用 CFv2 组件层次结构中的 /core/virtualization 提供核心分片。我们选择将其公开为 virtualization 分片,因为任何支持虚拟化的商品都会使用此分片。
然后,我们将 GuestLifecycle 协议公开给产品会话,并更新工作站产品会话以包含 TerminaGuestManager。
工具、诊断和开发者工效学
我们需要保留在核心产品上运行客机操作系统的能力。目前,我们使用通过 GN 参数手动添加到 build 中的其他核心分片来实现这一点。每个核心分片都支持单个访客。此提案中的任何内容都不需要更改其运作方式,但由于 vmm 和关联的设备负责管理进入来宾管理器分片的大部分 capability 路由,因此它大大简化了组件路由。
在日后的工作中,我们可以更改启动 GuestManager 组件的方式,以便进行开发。简单的访客(例如 debian 或 zircon)除了 GuestLifecycle 之外不需要任何其他功能,因此我们可以支持将这些组件启动到自己的集合中,以减少支持虚拟化工作流所需的自定义核心王国分片数量。
安全注意事项
vmm 需要一些特权功能才能正常运行(例如 HypervisorResource、某些 /dev 目录)。这种设计可避免将这些特权功能公开给会话。
与此设计相关的一个功能差异是,之前我们提供的协议代表单个虚拟机实例(例如 fuchsia.virtualization.TerminaGuestManager),而现在我们将提供使用 fuchsia.virtualization.GuestManager 协议创建任意数量的虚拟机实例的功能。此功能仅通过 vmm 组件公开,并且我们不允许会话将任意组件启动到包含 vmm 实例的集合中。
每当会话创建的任何访客的 GuestLifecycle 通道关闭时,系统都会停止该访客,以确保在用户会话停止后,没有任何访客继续运行。
为避免在 vmm 实例之间泄露状态,可变目录功能将从与每个实例关联的相应 GuestManager 组件动态路由到 vmm 实例,而不是例如静态路由共享目录功能。这样一来,会话还可以以一致的方式管理和保护有状态的虚拟机数据。
文档
产品如何使用虚拟化功能的详细信息将在 fuchsia.dev 上的虚拟化文档中新增的部分中记录。其中将详细介绍产品会话可以使用哪些 FIDL 协议,以及任何最佳实践。
测试
在此变更中,所有现有集成测试都将转换为使用 vmm_launcher 来演示正确的功能。我们还将探索对 vmm_launcher 进行模糊测试的可能方法,以验证 vmm 实例是否已路由共享的有状态功能。
考虑的替代方案
无需 VmmLauncher 组件
本文档中提出的 vmm_launcher.cm 不会执行任何有趣的操作,它只会在响应入站连接请求时在集合中创建组件。这可以由组件框架直接处理,这样我们就可以移除此组件。例如,为了支持这一点,组件框架可以提供一种创建同质组件集合的方法。组件在连接到这些集合时会自动启动,而不是在这些集合中创建动态子项。
添加一个专用组件来执行此操作并不需要做大量工作,但如果这是常见的模式,不妨考虑直接将其添加到组件框架中。
添加了显式 VmmLauncher 协议
我们可以创建一个名为的新的协议来供 VmmLauncher 使用,而不是在响应与现有 GuestLifecycle 协议的连接时隐式创建新的 vmm 组件。如果我们发现需要扩大 API 足迹以包含比目前提议的更多功能,则此设计会很合适。
library fuchsia.virtualization;
@discoverable
protocol VmmLauncher {
/// Launches a new, uninitialized virtual machine. The bound
/// `GuestLifecycle` can be used to initialize the VM and start or stop it.
///
/// The VM will be stopped and the component destroyed when the
///`GuestLifecycle` channel is closed.
Launch(resource struct {
lifecycle server_end:GuestLifecycle;
});
/// ... other functionality ...
};
由于我们目前不需要任何其他功能,因此我们更倾向于使用现有的一组协议。
