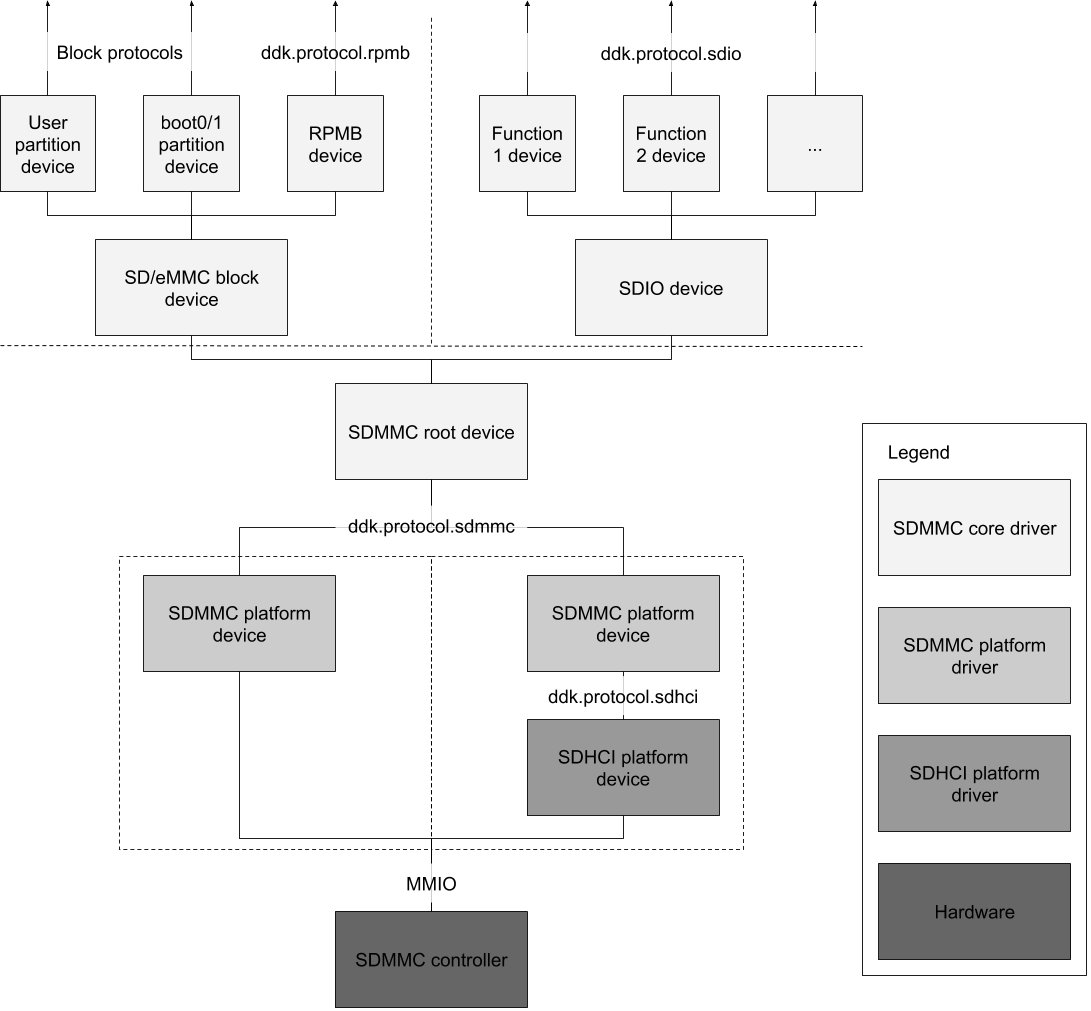
The SDMMC driver stack is divided into two main components: platform drivers that talk directly to controller hardware, and the core driver that handles protocol-specific device initialization and communication. The core driver is further divided into an SDIO driver and a block driver (for SD and eMMC). Each SDMMC controller has a different platform driver, while the core driver is used on all platforms.
Bringup
Bringing up an SoC with a new SDMMC controller requires writing a new platform
driver. If the controller implements the SDHCI specification then this driver
should implement
fuchsia.hardware.sdhci, otherwise it
should implement
fuchsia.hardware.sdmmc. It may be
helpful to disable DMA and higher speed modes through SdmmcHostInfo and
SdmmcHostPrefs until the basic functionality of the hardware has been
validated. See the SDHCI and SDMMC protocol definitions for more information.
SD/eMMC core driver
The SD/eMMC block driver creates a device that implements fuchsia.hardware.block.BlockImpl and fuchsia.hardware.block.partition for the user data partition, as well as devices for the boot0 and boot1 partitions if enabled (eMMC only). A device implementing fuchsia.hardware.rpmb is created if the device supports it (eMMC only, based on JEDEC standard JESD84-B51 section 6.6.22).
SDIO core driver
The SDIO core driver creates devices that implement fuchsia.hardware.sdio, one for each IO function. Whereas the only expected client of the SD/eMMC block driver is the storage stack, the SDIO driver will have different clients depending on what kind of SDIO card is detected. Client drivers bind to the SDIO core driver using the bind variables specified in the table below. Client drivers that use more than one IO function should bind to a composite device that has each function device as a fragment. Note that there could be multiple concurrent SDIO client drivers for combo cards, e.g. for Bluetooth and WiFi, in which case access to the bus will be shared through the core driver. Clients also cannot directly access function 0 to prevent possibly disrupting other clients. See the SDIO protocol definition for more information.
SDIO client binding
| Bind variable | Meaning |
|---|---|
BIND_SDIO_VID |
The IO function's manufacturer ID read from FBR |
BIND_SDIO_PID |
The IO function's product ID read from FBR |
BIND_SDIO_FUNCTION |
The IO function number from 1 to 7 |
Device diagram