Tracing tools enable visualization of input event dispatch paths. Each duration and outbound/inbound flow event must be curated to present an intuitive grasp of which components and function paths are involved in an event path.
Touch event flow
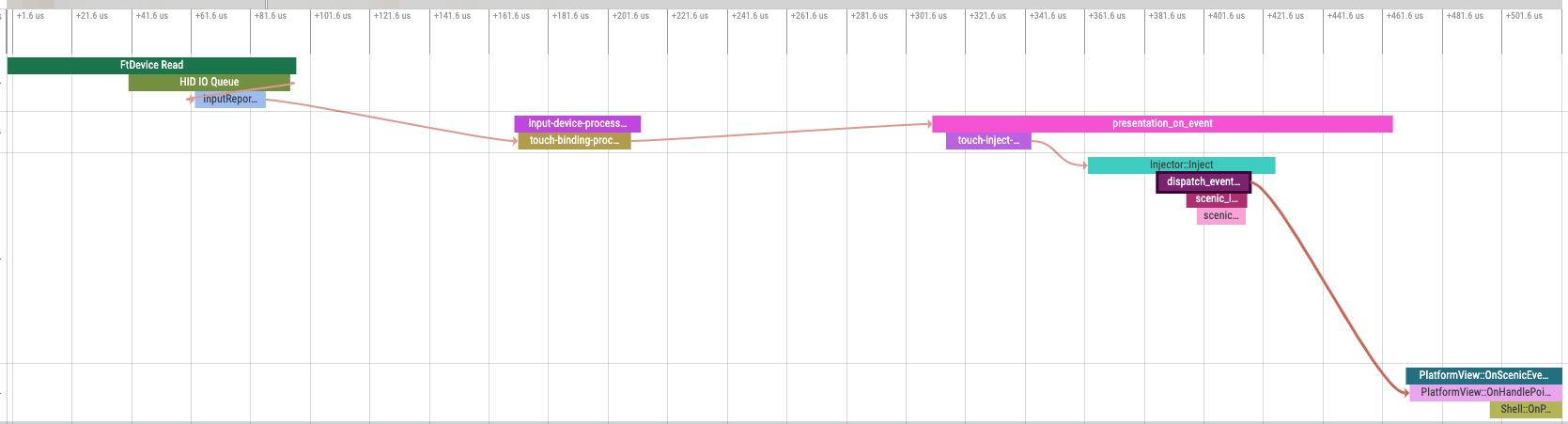
The touch event path involves a touch driver component, Input Pipeline, Scenic, and a fuchsia view component (Flutter, in this example). Each component occupies a horizontal strip, where its sequence of function call stacks are placed in chronological order.
The driver reads the touch event from the device and creates a fuchsia.input.report.InputReport. The driver's call stack is represented here with "HID IO Queue" and "InputReportInstance GetReports".
There is a flow event that connects "InputReportInstance GetReports" to the next duration in Input Pipeline, "touch-binding-process-reports". The FIDL protocol method is fuchsia.input.report.InputReportsReader.ReadInputReports().
There is a flow event that connects "touch-binding-process-reports" to "presentation_on_event", both within Input Pipeline. They are represented in separate function call stacks, because of the task loop arrangement in Input Pipeline's implementation.
The "presentation_on_event" naming is a legacy holdover to enable the trace-based metric input latency script to continue functioning. Owners are encouraged to change the names of durations and flows to match the actual intent, but may need to also update affected scripts. Typically, tracing computation scripts have a "smoke test" to prevent outright breakage, so a bad change should be caught by CQ.
There is a flow event that connects Input Pipeline's "touch-inject-into-scenic" to Scenic's "Injector::Inject" duration. The FIDL protocol method is fuchsia.ui.pointerinjector.Device.Inject(). The "touch-inject-into-scenic" duration is constructed to end on the Inject() call, to deliberately exclude the return acknowledgement. The overall "presentation_on_event" duration captures the return too, which accounts for its longer length.
The Scenic call stack consists of "Injector::Inject", "dispatch_event_to_client", and some other functions. There is a flow event that connects "dispatch_event_to_client" duration to Flutter's "PlatformView::OnHandlePointerEvent" duration. At the receiving side, the touch event has finally arrived and getting processed by a UI client component.
